The research
The situation today
Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) is one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality in women globally, with documented impacts on physical and mental health. Currently, healthcare management guidelines are limited to first aid, focusing on traumatic injuries and the immediate safety of victims.
There is no structured long-term health surveillance program, nor specific interventions that recognize IPV as a risk factor for chronic diseases.
Beyond visible injuries, IPV can lead to the development of conditions such as migraines, anxiety disorders, depression, insomnia, ulcers, and cardiovascular diseases.
The objectives
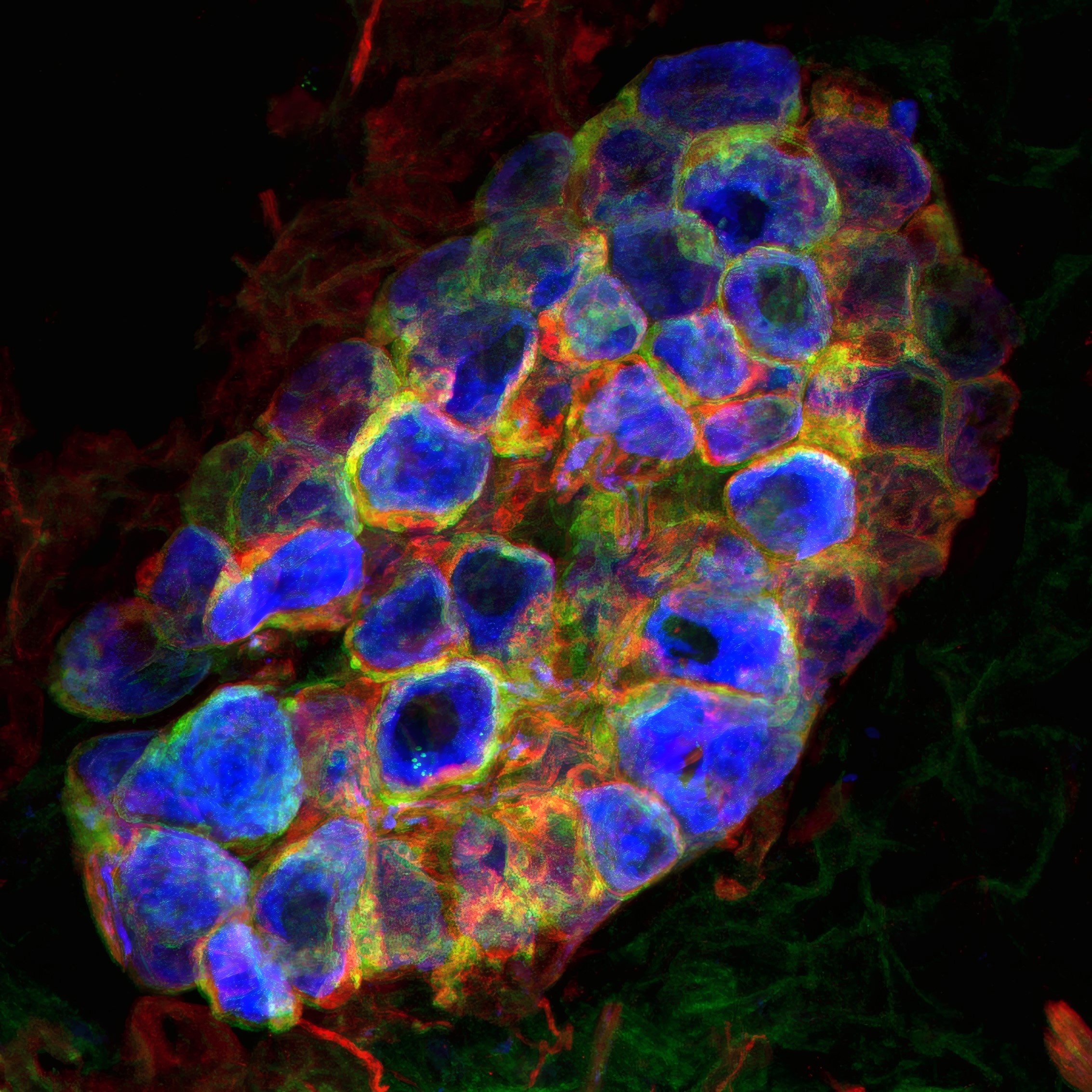
- Refine an experimental model to study IPV.
- Explore the molecular mechanisms of IPV-related damage at the cerebral and cardiac levels.
- Test possible therapeutic aids, both behavioral and pharmacological.
- Validate the findings from the animal model in women who are victims of IPV.
- Disseminate the knowledge obtained for training and prevention.